tp
Property Rental Manager - User Guide
Property Rental Manager (PRM) is a desktop application that helps property agents manage, filter and monitor single owner rental units for appropriate tenants. This application uses Command Line Interface (CLI) and is able to display information quickly with minimal latency. Also, the application is tailored to Singapore context.
- Quick Start
- Features
- Add Property:
add -property - Delete Property:
delete -property - List Properties:
list -property - List Properties with tags:
list -property TAG - Check Property:
check -property - Add Client:
add -client - Delete Client:
delete -client - List Clients:
list -client - List Clients With Tags:
list -client TAG - Check Client:
check -client - Pair Client and Property:
pair - Unpair Client and Property:
unpair - List Pairs:
list -pair - List Pairs Short:
list -pair -short - List Everything
list -everything - Find Client and Property:
find - Help Command:
help - Exit:
quit - Saving data
- Loading data
- Add Property:
- Command Summary
Quick Start
- Ensure that you have Java 11 or above installed.
- Download the latest version of
PropertyRentalManager.jarfrom here. - Put the JAR file into an empty folder.
- Open a command window and change the current working directory to the directory that the JAR file is located in using
following command:
cd [PATH_TO_JAR_DIRECTORY] - Run Property Rental Manager
java -jar PropertyRentalManager.jar
Features
Note:
- Parameters appear in the form of a/PARAMETER.
-propertyand-clientindicates whether the command is for property or client.- Words in UPPER_CASE are parameters to be specified by the user.
- Index values are limited to integers between 1 and 2147483647 (both inclusive).
Add Property: add -property
Adds a new property into property list, along with Singapore address and unit-type validations. Also, duplicate property entries of the same address will not be accepted.
Format: add -property n/NAME a/ADDRESS p/PRICE t/TYPE
Example: add -property n/Ash Ketchun a/25A Pallet Town, S121111 p/1600 t/LP BGL
Expected Output:
Adding a property with the following information:
Landlord: Ash Ketchun
Address: 25A Pallet Town, S121111
Renting Price: SGD1600/month
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
The descriptions of add -property PARAMETERS are as follows:
NAME: Name of property owner (Landlord)ADDRESS: Singapore Address (including postal code)PRICE: Rental Price per Month for property (SGD)TYPE: Type of property (e.g. HDB, Condominium, etc)
As there are validations involved, some PARAMETERS must adhere to specific formats as shown below:
For valid ADDRESS, a valid Singapore address must be provided with the following format and details:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Format:
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME], S[POSTAL CODE]
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME] #[unit level]-[unit number], S[POSTAL CODE]
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME] #[unit level]-[unit number] [building name], S[POSTAL CODE]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example:
60 Aria Street, S602580
101 Marlow Street #12-05, S059020
101 Marlow Street #12-05 Clife Parkview, S059020
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note:
1. Format requires single space between [DETAILS] (space sensitive).
2. [DETAIL] must be provided; [detail] is optional.
3. For landed property, treat [Block Number] as its unit number.
4. Any deviation from format will lead to invalid address.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For valid TYPE, one of the 15 valid Singapore-based unit type labels (App Pre-Defined) must be provided with the following format:
Format: t/<label>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HDB Labels:
<HDB 2> for HDB 2-Room Flexi
<HDB 3> for HDB 3-Room
<HDB 4> for HDB 4-Room
<HDB 5> for HDB 5-Room
<HDB 3Gen> for HDB Third-Generation
<HDB ExFlat> for HDB Executive Flat
<HDB DBSS> for HDB Design, Build and Sell Scheme (DBSS) Flat
<HDB ExMsn> for HDB Executive Maisonette
<HDB Jumbo> for HDB Jumbo Flat
<HDB TH> for HDB Terrace House
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Condominium Label:
<Condo> for Condominium
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Penthouse Label:
<PH> for Penthouse
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Landed Property Labels
<LP TH> for LP Terrace House
<LP SDH> for LP Semi-Detached House
<LP BGL> for LP Bungalow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lastly, for valid PRICE, a positive integer must be provided.
There is also another validation which checks for mismatch between address format and unit type of property. Certain unit types will require specific address format. Please refer to the description below:
1. Unit type with <LP> must not have #[unit level]-[unit number] in address.
Format:
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME], S[POSTAL CODE]
2. Unit type without <LP> must have #[unit level]-[unit number] in address.
Format:
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME] #[unit level]-[unit number], S[POSTAL CODE]
[BLOCK NUMBER] [STREET NAME] #[unit level]-[unit number] [building name], S[POSTAL CODE]
Note: HDB Terrace House (special case) is not restricted by any format.
DISCLAIMER:
Currently, there are some illogical inputs allowed by the application as shown below. Although validation can be done to prevent such cases, such validations will hinder normal operation and thus not implemented.
- Properties with the same street name but of different address format (with / without unit level and number) are allowed to be added.
- Properties with different street name but of the same postal code are also allowed to be added.
Delete Property: delete -property
Deletes the specified property from the property list and subsequently deletes any pairings involving that property.
Format: delete -property i/PROPERTY_INDEX
Example: delete -property i/2
Expected Output:
Deleting property with the following information:
Landlord: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Renting Price: SGD1000/month
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
List Properties: list -property
Lists all properties present in the list
Example:
list -property
Assuming that only 1 property is present in the list.
Expected output:
1. Landlord Name: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Property Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Property Rental Price: 1000
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There is 1 property in this list
List Properties With Tags: list -property TAG
Lists only selected details of all the properties, depending on the TAG. The commands for these are -
list -property a/This is for addresseslist -property n/This is for nameslist -property p/This is for priceslist -property t/This is for unit typeslist -property -shortThis is for the shorthand version(displays addresses, prices and unit types)
Example:
list -property p/
Assuming there are two properties in the list.
Expected output:1. 1000 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2. 2000 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- There are 2 properties in this list
Check Property: check -property
Displays the information of the specified property, along with the clients the property is being rented by, if any.
Format: check -property i/PROPERTY_INDEX
Example: check -property i/2
Expected Output:
Showing check results for this property:
Landlord: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Renting Price: SGD1000/month
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
Here are the tenants renting this property:
1. Client: Joseph Joestar
Contact Number: 83625471
Email: jojofirst@jmail.com
Budget: SGD9000/month
Number of entries in the list: 1
Add Client: add -client
Adds a new client into client list, along with Singapore contact number and basic email format validations. Also, duplicate client entries of the same name, contact number or email will not be accepted.
Format: add -client n/NAME c/CONTACT_NUMBER e/EMAIL b/BUDGET_MONTH
Example: add -client n/Gary Oaks c/90876543 e/garyoaks@example.com b/1550
Expected Output:
Adding a client with the following information:
Client: Gary Oaks
Contact Number: 90876543
Email: garyoaks@example.com
Budget: SGD1550/month
Note: Email is optional so excluding e/EMAIL or having e/BLANK is acceptable.
The descriptions of add -client PARAMETERS are as follows:
NAME: Name of client (Person looking for a property to rent)CONTACT_NUMBER: Contact number of clientEMAIL: Email of clientBUDGET_MONTH: Budget per month (SGD) of client
As there are validations involved, some PARAMETERS must adhere to specific formats as shown below:
For valid CONTACT_NUMBER, a Singapore contact number (no extension) must be provided. A Singapore contact number starts with a 6,8 or 9, followed by 7 remaining digits.
For valid EMAIL, it must adhere to the RFC 5322 Official Email Standard.
For valid BUDGET_MONTH, a positive integer must be provided.
Delete Client: delete -client
Deletes the specified client from the client list and subsequently deletes any pairings involving that client.
Format: delete -client i/CLIENT_INDEX
Example: delete -client i/3
Expected Output:
Deleting client with the following information:
Client: Doja Cat
Contact Number: 93437878
Email: doja88@example.com
Budget: SGD2000/month
List Clients: list -client
Lists all the clients present in the list
Example: list -client
Assuming that only 1 client is present in the list.
Expected output:
1. Client Name: Doja Cat
Client Contact Number: 93437878
Client Email: doja88@example.com
Client Budget: 2000
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There is 1 client in this list
List Clients With Tags list -client TAG
List only selected details of all the clients, depending on TAG. The commands for these are-
list -client c/This is for contact numberslist -client b/This is for budgetslist -client n/This is for nameslist -client e/This is for e-mailslist -client -shortThis is for the shorthand version(displays just names and budgets)
Example:list -client n/
Assuming that 2 clients are present in the list
Expected output:1. Doja Cat -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2. Doja Cat The Second -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- There are 2 clients in this list
Check Client: check -client
Displays the information of the specified client, along with the property the client is renting, if any.
Format: check -client i/CLIENT_INDEX
Example: check -client i/5
Expected Output:
Showing check results for this client:
Client: Doja Cat
Contact Number: 93437878
Email: doja88@example.com
Budget: SGD2000/month
Here is the property this client is renting:
Landlord: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Renting Price: SGD1000/month
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
Pair Client and Property: pair
Pairs the client to the specified property, to record that the client is renting the property.
Format: pair ip/PROPERTY_INDEX ic/CLIENT_INDEX
PROPERTY_INDEXandCLIENT_INDEXmust be indexes present in the client list and property list respectively.- The client must not currently be in a pairing.
- The property can be paired with multiple clients.
Example: pair ip/1 ic/5
Expected Output:
Pairing the following client and property:
Kujou Jotaro and 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Unpair Client and Property: unpair
Unpairs the client from the specified property, to record that the client is no longer renting the property.
Format: unpair ip/PROPERTY_INDEX ic/CLIENT_INDEX
PROPERTY_INDEXandCLIENT_INDEXmust be indexes present in the client list and property list respectively.- The client and property must currently be in the same pairing.
Example: unpair ip/1 ic/5
Expected Output:
Unpairing the following client and property:
Kujou Jotaro and 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
List pairs list -pair
Lists, in no particular order all information about clients and properties that have been paired.
The format for each such pair is -
Example: list -pair
Expected output:
Client:
Client Name: Doja Cat
Client Contact Number: 93437878
Client Email: doja88@example.com
Client Budget: 2000
Property:
Landlord Name: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Property Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Property Rental Price: 1000
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
List pairs short list -pair -short
Lists, in no particular order shortened information about clients and properties that have been paired.
The format for each such pair is -
Example list -pair -short
Expected output:
Client:
Client Name: Doja Cat
Client Budget: 2000
Property:
Property Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
Property Rental Price: 1000
List everything list -everything
Lists all information about every client and every property in the list.
Assume 1 client and 1 property is in the list and they are paired.
Example list -everything
Expected output:
1. Landlord Name: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Property Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Property Rental Price: 1000
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There is 1 property in this list
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pairs:
Client:
Client Name: Doja Cat
Client Contact Number: 93437878
Client Email: doja88@example.com
Client Budget: 2000
Property:
Landlord Name: Bob Tan Bee Bee
Property Address: 25 Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Property Rental Price: 1000
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There is 1 pair in this list
Find Client and Property: find
This feature allows for the queried text to be filtered. The queried text is not constrained within any field. This means that if the queried text matches the name of the first list and the address of second list, both entries will be counted as a match.
Format:
find -CLIENT/PROPERTY f/QUERY_TEXT
3 fields are required to be entered for successful operation:
- Command: In the context of this feature, the command will be
find - Client/Property: This section requires the selection of either client or property which is inputted after
-. - Query Text: After the tag
f/, enter the text that will be searched through.
Example:
find -property f/Bob The Builderfind -client f/Amos
The 1st command above search through the property list for any matches with Bob the Builder while the 2nd command
search through the client list for any matches with Amos.
Expected Output:
1. Landlord Name: Bob The Builder
Property Address: 25A Lower Kent Ridge Rd, S119081
Property Rental Price: 1000
Unit Type: LP Bungalow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Client Name: Amos
Client Contact Number: 91283543
Client Email: abc@examplemail.com
Client Budget: 1500
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Help Command: help
By entering the help command, users can see a condense version of the list of commands available while using the application. To invoke the help command, type help without any additional text.
The list of commands will be as show below:
The list of available commands are stated below:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LIST COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
list -client
list -property
list -everything
list -client <TAG>
list -property <TAG>
where <TAG> is replaced by the tag you would like to look into.
For example: list -client n/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ADD COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
add -client n/<CLIENT_NAME> c/<CONTACT_NUMBER> e/<EMAIL> b/<BUDGET>
add -property n/<LANDLORD_NAME> a/<ADDRESS> p/<RENTAL_PRICE> t/<UNIT_TYPE>
where the tags (represented by brackets) are replaced as accordingly
Note that email address is optional
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DELETE COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
delete -client i/<INDEX>
delete -property i/<INDEX>
where <INDEX> represents the index of entity to be deleted.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PAIR/UNPAIR COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pair ip/<INDEX> ic/<INDEX>
unpair ip/<INDEX> ic/<INDEX>
where <INDEX> represents the index of property and client to pair together with.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHECK COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
check -client i/<INDEX>
check -property i/<INDEX>
where <INDEX> refers to the index of the client or property to check for.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FIND COMMAND
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
find -client f/<QUERY_TEXT>
find -property f/<QUERY_TEXT>
where <QUERY_TEXT> refers to the text to search for in either client or property.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Exit: quit
Leaves the application with a goodbye message
Example: quit
Expected output:
Goodbye :). See you soon!
Loading data
The loading of the data occurs during the start of the program, before any command is entered. There will be 3 different loading operations:
- Client
- Property
- Pairing
Clients will be added to a list containing the clients if the data stored in client.txt conforms to the format.
Before appending into the list, it will also be passed through a check to ensure each of the entity is in the right
format. Should the data fail to be in the correct format, it won’t be stored into list.
Similar operation can be applied to the property list where the data is stored in property.txt. The entries will
also be checked that it was stored in the right format and each of the entries conforms to the requirement before it’s
added into the list containing all the property.
The pairing list will be the last to load. This is done so to verify that the client and property is within the
Client’s list and Property’s list respectively. In the scenario where either of the entries is not in, the pair
would not be loaded and will be considered as incorrect data inputted.
Saving data
Saving of data occurs in 3 instances of operation:
- Client is added to Client’s List
- Property is added to Property’s List
- Pair is added to Pairing’s List
When client, property and pairing is added, text will be appended to the text file as shown below:
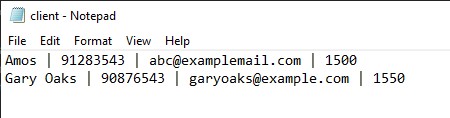
Client: AppendsCLIENT_NAME | CLIENT_CONTACT_NUMBER | CLIENT_EMAIL | CLIENT_BUDGETtoclient.txt.
An example of the client text file is as shown below:
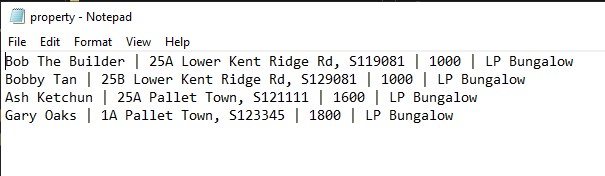
Property: AppendsLANDLORD_NAME | PROPERTY_ADDRESS | PROPERTY_RENTAL_RATE | PROPERTY_UNIT_TYPEtoproperty.txt.
An example of the property text file is as shown below:
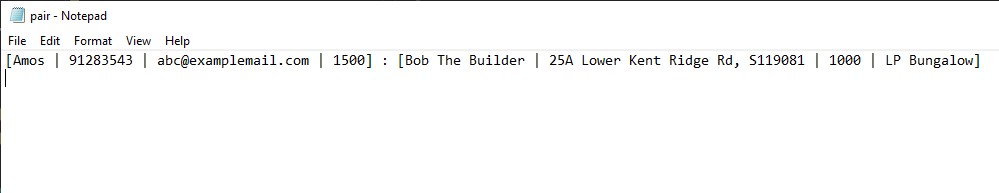
Pair: Appends[CLIENT_NAME | CLIENT_CONTACT_NUMBER | CLIENT_EMAIL | CLIENT_BUDGET] : [LANDLORD_NAME | PROPERTY_ADDRESS | PROPERTY_RENTAL_RATE | PROPERTY_UNIT_TYPE]topair.txt.
An example of the pairing text file is as shown below:
Updating data
Updating of data occurs in 6 instances of operation:
- Client is deleted from Client List -
delete -clientcommand invoked - Property is deleted from Property List -
delete -propertycommand invoked - Pair is removed from Pairing List -
unpaircommand invoked - Incorrect data identified when loading of Client from
client.txt - Incorrect data identified when loading of Property from
property.txt - Missing Client or Property when loading Pairs from
pair.txt
When the updating operation occurs, it will iterate through the list, depending on which list has been updated. While iterating through the list, the program will convert each entry into the correct format and store in their respective text files.
Manual input of data
Since the data is stored in a text file, it allows for user to manually key in the entries and will be loaded when the program is re-ran.
This is how the entries should be stored :
Client: CLIENT_NAME | CLIENT_CONTACT_NUMBER | CLIENT_EMAIL | CLIENT_BUDGET
Property: LANDLORD_NAME | PROPERTY_ADDRESS | PROPERTY_RENTAL_RATE | PROPERTY_UNIT_TYPE
Pairing: [CLIENT_NAME | CLIENT_CONTACT_NUMBER | CLIENT_EMAIL | CLIENT_BUDGET] : [LANDLORD_NAME | PROPERTY_ADDRESS |
PROPERTY_RENTAL_RATE | PROPERTY_UNIT_TYPE]
Note that if the entries are stored incorrectly, the program will automatically remove the entries from the text file during the next run of the program. This is done so to prevent overcrowding of junk data.
Command Summary
- Add Property:
add -property n/NAME a/ADDRESS p/PRICE t/TYPE - Delete Property:
delete -property i/PROPERTY_INDEX - List Properties:
list -property - List Property Addresses:
list -property a/ - List Property Owner Names :
list -property n/ - List Property Budgets:
list -property b/ - List Property Unit Type:
list -property t/ - List Property Short:
list -property -short - Check Property:
check -property i/PROPERTY_INDEX -
Find Property:
find -property f/QUERY_TEXT - Add Client:
add -client n/NAME c/CONTACT_NUMBER e/EMAIL b/BUDGET_MONTH - Delete Client:
delete -client i/CLIENT_INDEX - List Clients:
list -client - List Client Names:
list -client n/ - List Client Contact Numbers:
list -client c/ - List Client Budgets:
list -client b/ - List Client Emails:
list -client e/ - List Client Short:
list -client -short - Check Client:
check -client i/CLIENT_INDEX -
Find Client:
find -client f/QUERY_TEXT -
List Everything:
list -everything - Pair:
pair ip/PROPERTY_INDEX ic/CLIENT_INDEX - Unpair:
unpair ip/PROPERTY_INDEX ic/CLIENT_INDEX - List Pairs:
list -pair -
List Pairs Short:
list -pair -short - Help Command:
help